Code with VSquare
A Chronicle of Computer Education...
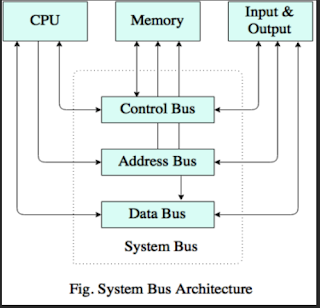
In the Computer Architecture, Bus is a collection of control lines,
address lines and data lines that transfer data between different computer
components inside computer. In other words, a set of parallel conductors
which allow the flow of instructions and data between different devices.
The name of the buses are generally decided by the type of signals it is
carrying or the method of operations. They are as follows:-
-
Data Bus:
-
Address Bus:
-
Control Bus:
It is bidirectional. Sometimes, it is also known as Memory bus. It handles
the transfer of all data and instructions between different functional areas
of computer system. The bidirectional data bus can only transmit in one
direction at a time. The data bus is used to transfer instructions from
memory to the C.P.U and memory as required by the instruction translation.
The data bus is also used to transfer data between memory and the
Input/Output devices during Input/Output operations.
It consists of all the signals necessary to define any of the possible
memory address location within the computer. An address is defined as label,
symbol or other set of characters used to designate a location or register
where the information is stored. Before data or instruction can be retained
or read from memory by the C.P.U. or Input/Output section. An address must
be transmitted to memory over a Address bus.
Fig: Control Bus
It is used by the C.P.U. to direct and monitor the action of the other
functional areas of the computer. It is used to transmit a variety of
individual signals like read, write, interpret, acknowledge, increment,
decrement and so on.. Necessary to control and coordinate the operations of
the computer. The individual signals transmitted over the control bus and
their functions are covered in the appropriate functional areas of
description.



Comments
Post a Comment